Publication and Exchange
#ARCs for Data Publication, Exchange, and Collaboration
The ARC framework provides an efficient system for managing research data publication, exchange, and collaboration, supporting researchers in adhering to FAIR principles (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable). In this context, it is important to clarify that FAIR does not necessarily mean open access. Accessibility in FAIR refers to the technical ability to access data, which can still be password-protected or restricted, as long as standard protocols are used.
#Data Publication and its Importance
The common vision in RDM is that, data publication should be a standard component of journal publications, with each journal article referencing the corresponding data publication. This practice offers several advantages to researchers, including:
- Increased citations: Data that is openly shared and referenced increases visibility and is more likely to be cited.
- Faster publication process: Well-documented and published data can streamline the review process, making it easier to evaluate research.
- Enhanced collaboration: Open science practices, including data sharing, foster transparency and collaboration across research fields.
- Publishable negative results: Data publication enables the sharing of negative or null results, which are often overlooked in traditional journals, but are valuable to the scientific community.
- Reduced redundant efforts: Publishing data prevents duplication of experiments, saving time and resources.
Data publications are ideally published as ARC Fair Digital Objects, using platforms that generate DOIs (Digital Object Identifiers) to permanently connect the data to a specific citation. These platforms ensure that data is stored for the long term, providing stable access and referenceability. One example is the Invenio platform, which is used by NFDI4Plants’ DataPLANT and connected to the ARC-powered PLANTdataHUB.
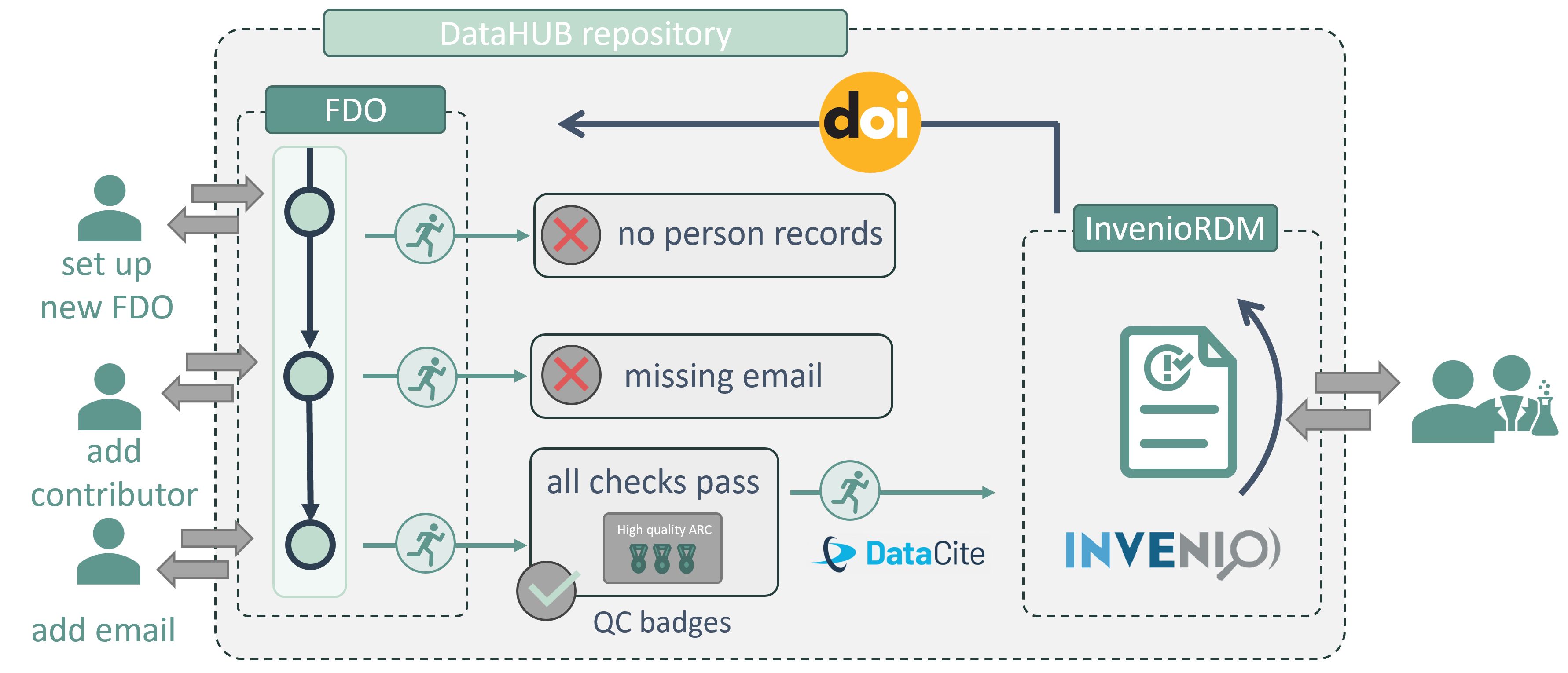
#Data Publication and Quality
Data publication platforms like ARC Data Hub can incorporate automatic validation processes, indicated by different quality badges, to ensure the quality of published data. This simplifies the process for researchers and reviewers, reducing the workload while improving trust in the data.
Moreover, when an ARC-powered data hub is connected to platforms like Invenio, it enables a community-driven peer review process, much like traditional journal reviews, to ensure that the published data meets the necessary standards. This provides an additional layer of validation, making the data more reliable and easier to reference.
#ARCs for Collaboration
In modern research, collaboration is essential, often involving teams with diverse roles and expertise. The ARC framework is well-suited to support collaborative research by providing multiple features that make data management and exchange more efficient:
- Layered information: ARC’s “everything is a file” approach allows for easy layering of additional information, making it simple to append metadata, corrections, or new results as the research evolves.
- High separability: The ARC’s natural branching structure reduces the likelihood of merge conflicts when multiple researchers contribute to the same project. This is particularly useful when collaborating across different teams or institutions.
- Collaborative research platform: ARCs provide a solid foundation for building collaborative research platforms, enabling seamless sharing of data between researchers. The ability to separate and merge different components of the ARC ensures that collaboration remains smooth and conflict-free.
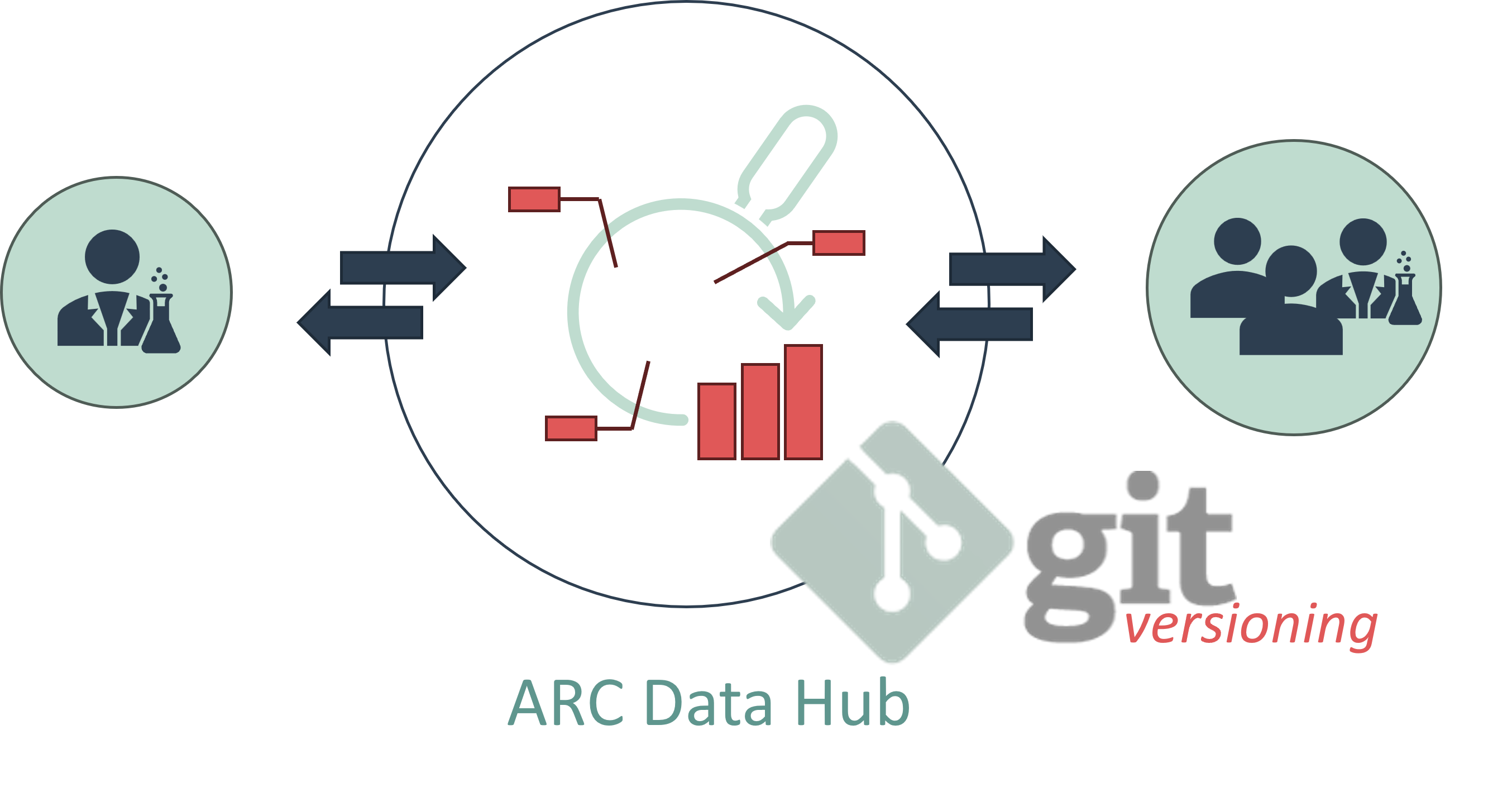
By using ARCs, researchers can easily collaborate on experiments, share data, and contribute to larger research projects, all while maintaining high standards of organization, documentation, and FAIRness. The ARC framework offers a robust and flexible tool for improving data management, quality, and collaboration in the modern scientific landscape.